
How Bariatric Surgery Changes Your Appetite And Metabolism?
Table of Contents:
Last Updated on November 15, 2023
There are several types of weight-loss surgery, or bariatric surgery, including gastric sleeve (sleeve gastrectomy), gastric bypass, and duodenal switch surgery. In addition to making your stomach smaller or restricting the amount of food that enters your stomach, bariatric surgery changes your body in a number of ways.
The more you learn about the different ways that bariatric surgery changes your body, both in helping get rid of excess weight and improving your quality of life, the more confident you can be in making the decision.
Bariatric Surgery Impact On Your Hunger, Appetite & Metabolism
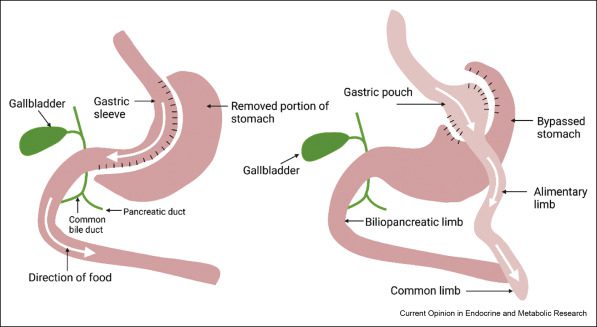
Contrary to the common belief that reducing stomach size is the sole reason for decreased appetite post-surgery, there’s more to the story. Procedures like gastric sleeve surgery play a crucial role in diminishing your appetite by lowering the production of ghrelin, a hormone responsible for inducing hunger. The surgical removal of a significant portion of the stomach that secretes ghrelin leads to a notable reduction in hunger pangs.
Understanding Ghrelin: The Hunger Hormone
Ghrelin, often referred to as the “hunger hormone,” is predominantly produced in the stomach. It plays a crucial role in signaling hunger to the brain. When the stomach is empty, ghrelin levels increase, prompting the sensation of hunger. Bariatric surgery, especially the gastric sleeve, involves removing a portion of the stomach that produces a significant amount of ghrelin. As a result, post-surgery patients experience a notable decrease in hunger pangs, making it easier to adhere to a reduced-calorie diet.
Changes in Leptin and Other Satiety Hormones
Leptin, another key hormone, is produced by fat cells and signals the brain to reduce appetite when fat stores are sufficient. In obese individuals, leptin sensitivity is often reduced, leading to an inability to feel full despite adequate food intake. Bariatric surgery can help reset this sensitivity, gradually restoring the body’s natural response to leptin and enhancing feelings of fullness.
The Role of Peptide YY and GLP-1
Peptide YY and GLP-1 (Glucagon-like peptide-1) are hormones released by the intestines after eating and are crucial in promoting a sense of satiety. Bariatric surgery can increase the levels of these hormones, further contributing to reduced appetite and improved control over eating behaviors.
Psychological and Behavioral Factors
It’s important to note that while hormonal changes play a significant role in reducing appetite, psychological and behavioral factors are also at play. Patients undergoing bariatric surgery often receive counseling and support to develop healthier eating habits and a new relationship with food. This holistic approach is vital for the long-term success of the surgery.
The Importance of Nutritional Counseling
Post-surgery, patients must adapt to a significantly reduced stomach capacity, which necessitates changes in eating patterns and food choices. Nutritional counseling is essential to ensure that patients meet their nutritional needs while adapting to their new appetite levels. This includes learning to recognize true hunger cues, understanding portion sizes, and choosing nutrient-dense foods to maintain energy levels and overall health.
Long-Term Effects and Monitoring
The long-term effects of these hormonal changes are a subject of ongoing research. Most patients experience a sustained decrease in appetite and an improved ability to control their eating. However, regular monitoring and follow-up are crucial to address any nutritional deficiencies or adjustments in dietary habits as the body adapts over time.
How Bariatric Surgery Affects Your Metabolism
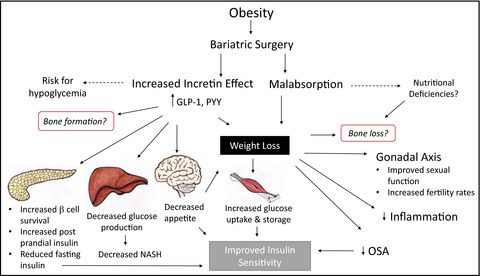
One of the least appreciated benefits of bariatric surgery is its effect on the metabolism of people with obesity. Excess weight and obesity can increase insulin resistance, inflammation and cell oxidation, all of which can negatively affect your energy levels and fat metabolism. So a positive side effect of weight reduction due to bariatric surgery is the improvement in your metabolism, which further helps you to lose weight.
Enhanced Insulin Sensitivity
One of the most significant metabolic changes post-bariatric surgery is the improvement in insulin sensitivity. Obesity is often associated with insulin resistance, a condition where the body’s cells don’t respond effectively to insulin, leading to elevated blood sugar levels. Post-surgery, as the body sheds excess weight, insulin sensitivity often improves, reducing the risk of type 2 diabetes and aiding in better blood sugar control. This change can be so profound that many patients with type 2 diabetes see a reduction or even remission of their condition.
Reduction in Inflammatory Markers
Chronic inflammation is a common issue in individuals with obesity, contributing to a range of health problems, including heart disease and metabolic syndrome. Bariatric surgery can lead to a significant reduction in markers of inflammation. This reduction is partly due to the decrease in fatty tissue, which is known to produce inflammatory substances. As inflammation decreases, the body’s overall metabolic health improves, enhancing energy levels and reducing the risk of various obesity-related conditions.
Improvement in Fat Metabolism
Obesity alters the body’s ability to metabolize fats efficiently. Bariatric surgery, by facilitating significant weight loss, can help normalize these processes. Improved fat metabolism not only contributes to further weight loss but also reduces the risk of fatty liver disease and improves lipid profiles, lowering the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
Changes in Gut Hormones and Microbiota
Bariatric surgery also affects gut hormones and the microbiota, both of which play crucial roles in metabolism. Changes in the gut flora post-surgery can improve energy harvest from food and impact how nutrients and calories are absorbed. Additionally, alterations in gut hormones can enhance metabolic rate and energy expenditure, further supporting weight loss and metabolic health.
Increased Basal Metabolic Rate
As patients lose weight post-surgery, there’s often an increase in the basal metabolic rate (BMR). This increase means the body uses more energy for basic functions at rest, which can contribute to further weight loss and help in maintaining the reduced weight long-term.
Long-Term Metabolic Monitoring
While the initial metabolic improvements post-surgery are significant, it’s essential for patients to engage in long-term monitoring. Regular check-ups and metabolic assessments ensure that these benefits are sustained and any potential deficiencies or issues are addressed promptly.
The Role of Lifestyle Changes
It’s important to note that while bariatric surgery initiates metabolic improvements, sustaining these benefits requires lifestyle changes. A balanced diet and regular physical activity are crucial in maintaining the improved metabolic state and ensuring overall health and well-being.
How Bariatric Surgery Helps Improve Your Diet
Another positive side-effect of bariatric surgery reported by participants in a number of studies is a change in the taste and even smell of certain foods following the procedure. As many as 97% of participants in one study reported at least one of the effects, which include an increased sensitivity to eating and drinking sweet, sour and/or fatty foods and beverages.
The heightened sensitivity reduces your cravings for fast foods and sweet, high-carbohydrate foods and drinks. The same sorts of foods and drinks that are most often linked to weight gain.
For more information, please contact our team at The Sleeve Clinic where we’ll be happy to provide you with more resources.
Nutritional Guidance Post-Surgery
Post-bariatric surgery, patients must adhere to a specific nutritional regimen to ensure proper healing and effective weight loss. This includes a diet rich in proteins, vitamins, and minerals, and low in sugars and fats. Emphasizing the importance of a balanced diet and regular consultations with a nutritionist can be a valuable addition to the content.
Psychological Impact and Support
The psychological impact of drastic weight loss and body changes post-surgery is profound. Addressing the need for psychological support and counseling can provide a holistic view of the journey. Discussing support groups and mental health resources can be beneficial for potential patients.
Physical Activity and Lifestyle Changes
Incorporating content about the importance of physical activity post-surgery can be enlightening. Highlighting tailored exercise regimes and the role of physical activity in maintaining weight loss and overall health would be a valuable addition.
Long-term Health Benefits
Expanding on the long-term health benefits of bariatric surgery, such as improved cardiovascular health, remission of type 2 diabetes, and alleviation of sleep apnea, can provide readers with a comprehensive understanding of the surgery’s impact.
Research Papers/Citations
Fenske, W., Athanasiou, T., Harling, L., Drechsler, C., Darzi, A., & Ashrafian, H. (2013). Obesity-related cardiorenal disease: the benefits of bariatric surgery. Nature Reviews Nephrology, 9, 539-551. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneph.2013.145.
Tu, J., Wang, Y., Jin, L., & Huang, W. (2022). Bile acids, gut microbiota and metabolic surgery. Frontiers in Endocrinology, 13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2022.929530.
Gralka, E., Luchinat, C., Tenori, L., Ernst, B., Thurnheer, M., & Schultes, B. (2015). Metabolomic fingerprint of severe obesity is dynamically affected by bariatric surgery in a procedure-dependent manner.. The American journal of clinical nutrition, 102 6, 1313-22 . https://doi.org/10.3945/ajcn.115.110536.
Related Reads





